实现精美页面是前端工程师的核心能力之一,CSS布局技术是实现精美页面的核心技术,但CSS布局好入门,难精通。实际工作中经常遇到各种各样的布局方式,常用的主流布局方案:flex弹性布局、grid网格布局、响应式布局。熟练掌握各类布局方式在实际开发中能起到事半功倍的效果。
flex弹性布局
不定项水平居中布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<style>
* {padding: 0; margin: 0;}
.box {
width: 300px;
background: violet;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.box div {
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background: pink;
border-radius: 50%;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>
<!-- 不定项水平居中布局: 不定数量的子项水平居中对齐 -->
<div class="box">
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
均分列布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24<style>
* {padding: 0; margin: 0;}
.box {
width: 300px;
background: violet;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
/* justify-content: space-around; */
/* justify-content: space-evenly; */
}
.box div {
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background: pink;
border-radius: 50%;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>
<!-- 均分列布局: 子项按需求平均分配剩余空间 -->
<div class="box">
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
子项分组布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33<style>
* { padding: 0; margin: 0;}
.box {
width: 500px;
height: 60px;
background: violet;
padding: 0 20px;
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
align-items: center;
}
.box div {
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background: pink;
margin-left: 10px;
}
.box div:nth-of-type(1) {
margin-left: 0;
margin-right: auto;
}
.box div:nth-of-type(3) {
margin-right: auto;
}
</style>
<!-- 子项分组布局: 子项按分组分开布局 -->
<div class="box">
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
等高布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19<style>
* {padding: 0;margin: 0;}
.box {
width: 500px;
background: violet;
padding: 10px 20px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.box div {
width: 100px;
background: pink;
}
</style>
<!-- 左右等高布局: 左右高度自适应, 任意一侧高度增加可使两侧高度保持一致 -->
<div class="box">
<div>左右等高布局</div>
<div>左右高度自适应, 任意一侧高度增加可使两侧高度保持一致</div>
</div>
两列与三列布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14<style>
* { padding: 0; margin: 0; }
.box { display: flex; height: 100vh; }
.box .col1,.box .col3 { width: 100px; background: pink; }
.box .col2 { flex: 1; background: violet; }
</style>
<!-- 两列与三列布局: 自适应部分设置 flex-grow: 1 即可
两列: 左边固定 + 右边自适应
三列: 左右固定 + 中间自适应 -->
<div class="box">
<div class="col1">左侧固定宽度</div>
<div class="col2">中间自适应宽度</div>
<div class="col3">右侧也是固定宽度</div>
</div>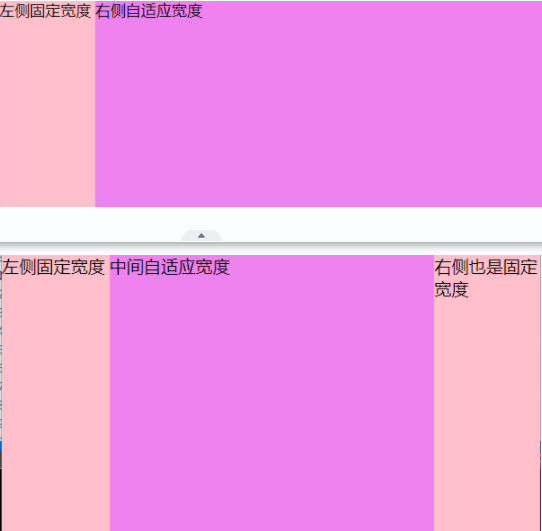
stickyfooter布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27<style>
* { padding: 0;margin: 0; }
.box {
height: 100vh;
width: 100%;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.content {
font-size: 20px;
background: pink;
flex: 1;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 50px;
background: violet;
}
</style>
<!-- stickyfooter布局: 底部按钮 内容区域不足一屏时,固定在底部,内容多时随内容滚动 -->
<div class="box">
<div class="content">stickyFooter布局, 内容少时, 按钮固定粘贴在底部, 当内容多时, 按钮会被推到底部, 随页面滚动stickyFooter布局,
内容少时, 按钮固定粘贴在底部, 当内容多时, 按钮会被推到底部, 随页面滚动stickyFooter布局, 内容少时, 按钮固定粘贴在底部, 当内容多时,
固定粘贴在底部, 当内容多时,按钮会被推到底部, 随页面滚动stickyFooter布局, 内容少时, 按钮固定粘贴在底部, 当内容多时, </div>
<div class="footer">底部按钮</div>
</div>
grid网格布局
Grid是二维布局,将容器划分成行和列,产生单元格,根据设计需求将内容区块放置到单元格中
基本网格
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26<style>
.main {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
background: skyblue;
display: grid;
/* 单独定义行和列 */
grid-template-columns: 80px auto 100px;
grid-template-rows: 25% 100px auto 60px;
/* 简写一 */
grid-template: 25% 100px auto 60px/80px auto 100px;
/* 简写二 */
grid: 25% 100px auto 60px/80px auto 100px;
}
.main div {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
border: 1px solid pink;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div>
<div>7</div><div>8</div><div>9</div><div>10</div><div>11</div><div>12</div>
</div>
</body>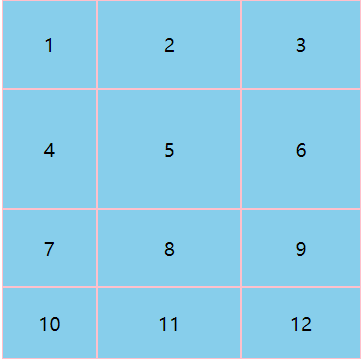
合并单元格的网格
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46<!-- 使用命名方式定义网格区域,可以合并单元格,子项需配合grid-area属性进行使用 -->
<style>
.main {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
background: skyblue;
display: grid;
/* grid: 25% 100px auto 60px/80px auto 100px;
grid-template-areas:
"a1 a1 a2"
"a1 a1 a2"
"a3 a3 a3"
"a4 a5 a5"; */
/* 简写 */
grid: "a1 a1 a2"25% "a1 a1 a2"100px "a3 a3 a3"auto "a4 a5 a5"60px / 80px auto 100px;
}
.main div {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
border: 1px solid pink;
}
.main div:nth-of-type(1) {
grid-area: a1;
}
.main div:nth-of-type(2) {
grid-area: a2;
}
.main div:nth-of-type(3) {
grid-area: a3;
}
.main div:nth-of-type(4) {
grid-area: a4;
}
.main div:nth-of-type(5) {
grid-area: a5;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div>4</div>
<div>5</div>
</div>
</body>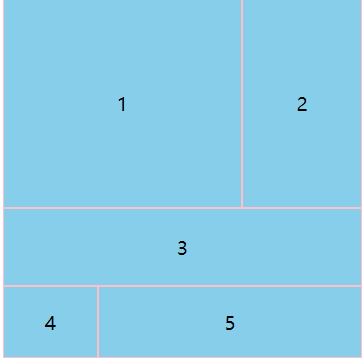
比定位更方便的叠加布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33<style>
.main {
margin: 50px auto;
display: grid;
width: 646px;
height: 403px;
}
.main img,
.main span,
.main p {
grid-area: 1/1/1/1;
font-size: 16px;
color: darksalmon;
}
.main p {
color: darksalmon;
align-self: end;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .5);
padding: 5px 10px;
font-size: 16px;
}
.main span {
justify-self: end;
margin: 10px 10px 0 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="main">
<img src="./grid.jpg" alt="">
<span>grid布局</span>
<p>使用grid代替position定位实现叠加效果布局</p>
</div>
</body>
响应式布局
指网页能自动识别屏幕宽度、并作出相应调整的网页设计。响应式布局可以为不同终端的用户提供更加舒适的界面和更好的用户体验
媒体查询
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32<!-- 媒体类型: 描述设备的一般类别 -->
all: 适用所有设备
print: 适用于打印预览模式
screen: 主要用于屏幕
speech: 主要用于语音合成器
<!-- 媒体特性: 描述了user agent 输出设备 浏览器环境的具体特征 -->
width: viewport的宽度
height: viewport的高度
aspect-radio: viewport的宽高比
orientation: viewport的旋转方向 portrait 横屏 landscape 竖屏
<!-- 逻辑操作符: 用于联合构造复杂的媒体查询 -->
and: 将多个媒体查询规则组合成单条媒体查询
not: 用于否定媒体查询, 不满足返回为true 否则返回false
only: 用于旧版浏览器识别媒体类型使用
逗号(,): 用于将多个媒体查询合并为一个规则
<style>
/* 在竖屏模式下生效 */
@media (orientation: landscape){
.box { width: 200px; background: pink; }
}
/* 屏幕宽度在700px到1200px之间生效 */
@media screen and (min-width: 700px) and (max-width: 1200px){
.box { width: 200px; background: pink; }
}
/* 在屏幕和打印模式且最小宽度为700px的模式下生效 */
@media screen, print and (min-width: 700px) {
.box { width: 200px; background: pink; }
}
</style>
<!-- link标签方式: 通过media属性设置媒体查询类型和媒体特性 -->
<link ref="stylesheet" href="css/index.css" media="(orientation: landscape)" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index.css" media="screen and (max-width:600px)" />媒体查询的编写位置及顺序
1
2
3
4
5<!-- 1. 添加到样式表的底部, 对css进行优先级的覆盖 -->
<!-- 2. 移动端 -> PC端的适配规则: min-width从小到大 -->
min-width方式, 多条件时从小到大适配. 移动优先原则, 先编写移动设备样式, 然后再过渡到PC端
<!-- 3. PC端 -> 移动端的适配规则: max-width从大到小 -->
max-width方式, 多条件时从大到小适配. 先编写PC端样式, 然后再过渡到移动端响应断点(阈值)的设定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21<!-- 常见响应断点阈值 -->
extra small < 576px 移动手机端
small >= 576px -sm 小屏幕
medium >= 768px -md 中等屏幕
large >=992px -lg 大屏幕
x-large >=1200px -xl 较大屏幕
xx-large >=1400px -xxl 超大屏幕
<style>
.d-none { display: none }
@media (min-width: 576px) { .d-sm-none { display: none }}
@media (min-width: 768px) { .d-md-none { display: none }}
@media (min-width: 992px) { .d-lg-none { display: none }}
@media (min-width: 1200px) { .d-xl-none { display: none }}
@media (min-width: 1400px) { .d-xxl-none { display: none }}
</style>
<div class="d-none">1111</div>
<div class="d-sm-none">2222</div>
<div class="d-md-none">3333</div>
<div class="d-lg-none">4444</div>
<div class="d-xl-none">5555</div>
<div class="d-xxl-none">6666</div>响应式栅格系统
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33<style>
.row {
background: skyblue;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(12, 1fr);
grid-template-rows: 50px;
grid-auto-rows: 50px;
}
.row div {
background: pink;
border: 1px solid #000;
grid-area: auto/auto/auto/span 12;
}
@media (min-width: 576px) {
.row .col-sm-6 { grid-area: auto/auto/auto/span 6; }
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.row .col-md-4 { grid-area: auto/auto/auto/span 4; }
}
@media (min-width: 992px) {
.row .col-lg-3 { grid-area: auto/auto/auto/span 3; }
}
</style>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
<div class="col-sm-6 col-md-4 col-lg-3">col</div>
</div>