vuex和vue-router是vue生态系统中的很重要的两个工具。vuex 是vue用来管理数据状态的一种机制,将Vue中所有的状态(数据)抽离出来进行统一管理。Vue Router 是 Vue.js 官方的路由管理器。它和Vue.js的核心深度集成,让构建单页面应用变得易如反掌,是SPA(单页应用)的路径管理器。
Vuex
Vuex是一个专门为vue.js应用程序开发的状态(数据)管理模式.它采用集中式存储应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化.
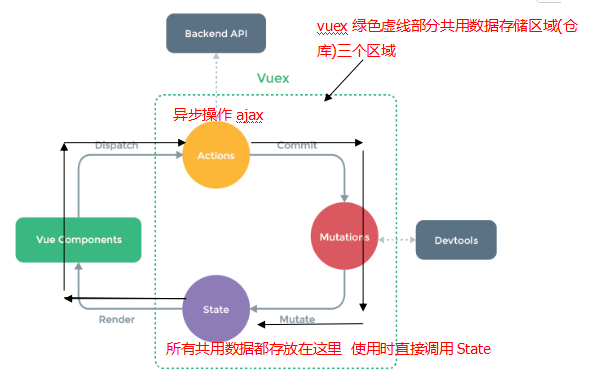
Vuex使用场景:多个视图依赖于同一状态或相同数据, 来自不同视图的行为需要
使用方式
npm install vuex -S安装vuex模块import Vuex from 'vuex'引入vuex模块Vue.use(Vuex)作为插件使用new Vuex.Store()定义store容器new Vue({store})注入到根实例中1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12// src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex) // 将vuex作为插件使用
let store = new Vuex.store({}) // 定义store容器
export default store // 将store导出
// main.js
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, // 将store注入到根实例中
})
Vuex核心概念
- Store 类似容器 包含应用的大部分状态 不建议直接修改state中的状态 使用提交mutations显式修改
State 包含所有应用级别状态的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7// 定义store容器
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { conut: 10 }
})
// 组件内取出状态(数据) hello.vue
this.$store.state.count
//Getters 对state数据进行处理 在组件内部获取store中的状态函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
shopList: [{
id: 123, count: 20
},{
id: 124, count: 30
}]
},
getters: { // gettres可以定义为一个函数
total(state){
return state.shopList.reduce((prev, item) => prev + item.count, 0)
}
}
})
//xx.vue 中使用
this.$store.getters.totalMutation vuex的state状态更新的唯一方式提交mutations
Mutation主要包含两部分 type 字符串的事件类型 handle该回调函数的第一个参数就是statemutation必须是同步更新状态,不要在mutation中进行异步的操作1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13mutations: {
// 第一个默认参数是state 第二个参数 payload是commit传递过来的值 可以是对象
updateCount(state, payload){
state.count += payload.add
}
}
methods: {
// 修改store中state的数据 提交一个mutations
// 如果不包含异步操作 可以直接在组建中 使用commit提交mutations
changeState(){
this.$store.commit('updateCount', {add: 5})
}
}Action 包含异步操作都放在action里面 提交mutations改变状态
context是和store对象具有相同方法和属性的对象,在action中可以通过context进行commit一个mutations操作,也可以获取context.state等。在vue组件中调用 this.$store.dispatch(‘action’)去触发action。可以将异步操作放在一个Promise中,并且成功或者失败后,调用对应的resolve或reject1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19// action 中返回一个promise
actions: {
increment(context) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => { // 异步操作
context.commit('incrementMutation')
resolve()
}, 2000)
})
}
}
methods: {
incrementHandle(){
// 派发action操作
this.$store.dispatch('increment').then(res => {
console.log('完成更新操作')
})
}
}Module 模块
Vuex允许我们将store分割成模块(Module), 而每个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getters等module下的局部状态通过state获取, 根节点(全局)的状态则通过rootState获取1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9// 获取全局的state
const moduleA = {
action: {
test({state, commit, rootState}){}
},
getters: {
test(state, getters, rootState){}
}
}使用
vuex-persistedstate实现vuex持久化vuex 是 vue 的状态管理器,存储的数据是响应式的。但是并不会保存起来,刷新之后就回到了初始状态, 使用此插件可以将state存储到localstorage或sessionstorage中1
2
3
4
5
6import createPersistedState from "vuex-persistedstate"
const store = new Vuex.Store({
plugins: [createPersistedState({
storage: window.sessionStorage
})]
})
Vuex的工具函数/语法糖/钩子函数
...mapState(['count'])取state中的数据...mapGetters(['total'])对state数据的处理...mapMutations(['updateCount'])调用mutations执行同步操作...mapActions(['updateCountSync'])调用action提交mutations执行异步操作1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16// index.vue
import { mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions } from 'vuex'
new Vue({
computed(){ // mapState 和 mapGetters 需要放在computed中
...mapState(['count']), // 后面还有内容时 需要加上 逗号,state数据放在字符串数组中
...mapState('goods', ['count']), // 有modules
...mapGetters(['total']),
...mapGetters('goods', ['total']), // 有modules
},
methods: { // mapMutations 和 mapActions 需要放在 methods中
...mapMutations(['updateCount']), // 后面还有内容时 需要加上 逗号,方法放在字符串数组中
...mapMutations('goods', ['updateCount']), // 有modules
...mapActions(['updateCountSync']),
...mapActions('goods', ['updateCountSync']), // 如果是某个modules下action需要加namespaced命名空间
}
})
vuex实现原理
使用 Vue 实例管理状态,只能在vue中使用
Vue Router
vue-router实现原理
- SPA(single page application) 单页面应用程序 页面url改变, 但页面不进行整体的刷新
Hash模式
1
2// vue-router 默认 hash 模式 hash模式会在url中自带#
// Hash模式通过锚点值的改变,根据不同的值,渲染指定DOM位置的不同数据。hash 模式的原理是 onhashchange 事件(监测hash值变化)History模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7// 用路由的 history 模式,只需要在配置路由规则时,加入"mode: 'history'",这种模式充分利用了html5 history interface 中新增的 pushState() 和 replaceState() 方法。
// 对历史记录修改的功能。只是当它们执行修改时,虽然改变了当前的 URL ,但浏览器不会立即向后端发送请求
// 需要后台配置支持 后台没有正确的配置 就会返回 404 如nginx配置
/* location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
} */
// {path: "*", redirect: "/"}] 前端路由设置 如果URL输入错误 路由不存在 自动跳到到首页 或设置404页面
基础配置
- 安装
npm install vue-router --save 配置路由文件
router/index.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46// router/index.js
// 引入vue-router插件
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 安装路由插件router
Vue.use(Router)
// 生成路由实例
// Router 常用参数
// routes: [] 路由信息 mode: 'hash' 路由模式 linkActiveClass: 'highlight' 路由高亮
// scrollBehavior(to,from,savedPosition) 滚动行为 fallback:true 对于不支持history路由时, 自动跳转到hash模式下
let router = new Router({ // 配置组件和路由的映射关系
// 定义路由模式 默认为 hash
mode: 'history', // 需要后端配合
// 设置当前路由高亮样式
linkActiveClass: 'is-active',
// 配置组件和路径的映射关系 routes 常见参数
// path: '/home' redirect: '/app' 重定向 name: 路由名称 component: 'todo' 路由组件
// meta: 元信息 设置meta信息 children: [{}] 子路由 嵌套路由
routes: [{
path: '/',
redirect: '/index' // 将根路径重定向到首页
}, {
path: '/index',
name: Home,
component: Home
}, {
path: '/Management',
name: 'Management',
component: Layout,
children:[{
path: '/project',
name: 'Project',
component: Project,
meta: {
login: true,
title: '标题',
auth: true
}
}]
}]
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router, // 将路由挂载到Vue实例中
})
// app.vue 中
<router-view>路由对应组件显示的位置</router-view>通过
<router-link>和<router-view>使用声明式路由<router-view />组件显示的位置<router-link to="/index" tag="li">主页</router-link>跳转链接tag可以指定<router-link>之后渲染成什么标签,默认是a
编程式导航跳转
this.$router.push() 会向history栈添加一个新的记录并导航到改URL下
this.$router.push('index')字符串this.$router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: '123' }})命名的路由使用的是name和params如果使用path则params无效this.$router.push({ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }})带查询参数使用的是path和querythis.$router.replace()它不会向 history 添加新记录, 替换掉当前的 history 记录。this.$router.go(n)在 history 记录中向前或者后退多少步this.$router.go(1)在 history 记录中前进一步,等同于 history.forward()this.$router.go(-1)在 history 后退一步记录,等同于 history.back()
$router与$route
- $router 路由实例对象 使用new VueRouter创建的实例,包括了路由的跳转方法,钩子函数等。常用于编程式导航
$route 当前路由信息对象 在组件内部可以通过 this.$route 的方式进行调用。
1
2
3
4
5
6// 1. $route.fullPath 为当前路由的全路径
// 2. $route.path 为当前路由的绝对路径
// 3. $route.params 包含路由中动态片段和全匹配片段的键值对
// 4. $route.query 包含路由中查询参数的键值对
// 5. $route.name 当前路由设置的name属性。
// 6. $route.meta 当前路由元信息$route与$router的区别
$router为VueRouter实例,想要导航到不同URL,则使用$router.push方法$route为当前路由对象,里面可以获取name、path、query、params等
滚动行为
1 | //点击浏览器的前进后退或切换导航时触发 |
路由传参
传递参数方式一: <router-link>1
2
3
4
5
6<router-link
:to="{
path: '/detial/:id' // params形式
query: { name: 'tew', age: '28' } // query模式
}"
>简介</router-link>
传递参数方式二: JavaScript代码1
2
3
4this.$router.push({
path: '/detial/:id',
query: { name: 'tew', age: '28' }
})
传递参数主要有两种类型: params和query1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12/*
params的类型:
配置路由格式: /router/:id
传递的方式: 在path后面跟上对应的值
传递后形成的路径: /router/123, /router/abc
通过this.$route.params 获取params方式参数
query的类型:
配置路由格式: /router, 也就是普通配置
传递的方式: 对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
传递后形成的路径: /router?id=123, /router?id=abc
通过this.$route.query 获取query方式参数
*/
路由导航守卫
全局路由导航守卫
- router.beforeEach(to, from, next) 全局前置守卫 常用beforeEach来完成页面标题的修改.
- router.beforeResolve(to, from, next) 全局解析守卫
- router.afterEach(to, from, next) 全局后置守卫
1 | // 每个守卫方法接收三个参数 |
路由独享的守卫
在路由配置上直接定义 beforeEnter1
2
3
4
5
6
7const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [{
path: '/foo',
component: Foo,
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {}
}]
})
组件内的守卫
- beforeRouteEnter
- beforeRouteUpdate 路由参数更新时触发 详情页面id变化 mounted里的函数只执行一次的问题 可以代替watch
- beforeRouteLeave
1 | const Foo = { |
使用router.addRoutes动态添加路由
1 | this.$router.addRoutes([{ |
路由守卫触发过程
- 导航被触发
- 调用全局的beforeEach前置守卫
- 在重用的组件里调用beforeRouterUpdate守卫
- 在路由配置里面调用路由独享守卫
- 调用被激活组件的beforeRouterEnter守卫
- 调用全局的beforeResolve守卫
- 调用全局的afterEach后置守卫
- 触发DOM更新
keep-alive与 vue-router
1 | // keep-alive 是 Vue 内置的组件,可以使被包含的组件保留状态,或避免重新渲染。 |
vue项目实现按需加载或懒加载的3种方式
- 路由懒加载的主要作用就是将每个路由对应的组件打包到单独的js中.只有在这个路由被访问到的时候, 才加载对应路由的js文件
vue异步组件 AMD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12// vue-router配置路由 , 使用vue的异步组件技术 , 可以实现按需加载 .
// 但是,这种情况下一个组件生成一个js文件
/* vue异步组件技术 */
{
path: '/home',
name: 'home',
component: resolve => require(['@/components/home'],resolve)
}, {
path: '/index',
name: 'Index',
component: resolve => require(['@/components/index'],resolve)
}路由懒加载(使用import)
1
2
3
4
5
6// 没有指定webpackChunkName,每个组件打包成一个js文件。
/* const Home = () => import('@/components/home')
const Index = () => import('@/components/index')
// 指定了相同的webpackChunkName,会合并打包成一个js文件。 把组件按组分块*/
const Home = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: 'ImportFuncDemo' */ '@/components/home')
const Index = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: 'ImportFuncDemo' */ '@/components/index')webpack的require.ensure()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// 使用webpack的require.ensure, 多个路由指定相同的chunkName,会合并打包成一个js文件。
{
path: '/home',
name: 'home',
component: r => require.ensure([], () => r(require('@/components/home')), 'demo')
}, {
path: '/index',
name: 'Index',
component: r => require.ensure([], () => r(require('@/components/index')), 'demo')
}